The Gastrointestinal System An Introduction Biology Diagrams This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Anatomy and Physiology of the Gastrointestinal System essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently.

The upper gastrointestinal tract consists of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. [13] The exact demarcation between the upper and lower tracts is the suspensory muscle of the duodenum.This differentiates the embryonic borders between the foregut and midgut, and is also the division commonly used by clinicians to describe gastrointestinal bleeding as being of either "upper" or

Anatomy and Physiology of the Gastrointestinal System Notes Biology Diagrams
Learn about the anatomy and functions of the gastrointestinal tract, a series of hollow organs from the mouth to the anus. The web page covers the oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, appendix, cecum, colon, rectum and anal canal.

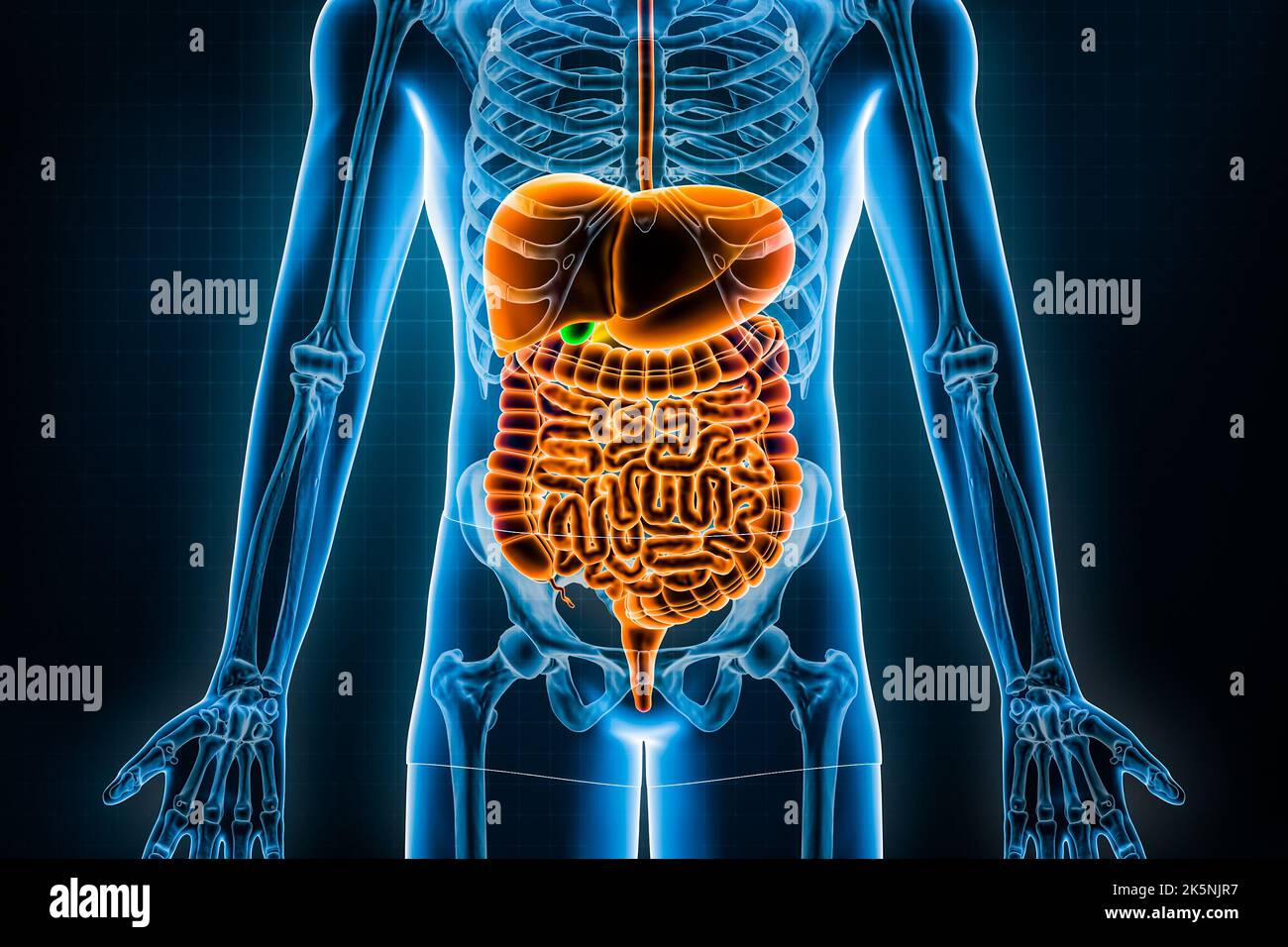
The gastrointestinal system (GI) is critical in maintaining a healthy body by eliminating waste and absorbing nutrients through a variety enzymes and hormone processes. The baseline knowledge of this body system will significantly support your future success in the nursing program. Your digestive system sends food on an incredible journey through your body. Digestion is a complicated process. It involves many organs working together. These organs pull the nutrients from what you eat and drink that your body needs. Keeping your digestive system healthy and working well supports your overall health.

Definition, Organs, Diagram, & Facts Biology Diagrams
Functions of the digestive system Trigger and initiation. The function of the digestive system truly begins within the brain.Whenever the body's energy stores (i.e. blood glucose, protein, or fat stores) fall below a set point, the hunger centres of the hypothalamus are activated. These centres regulate satiety (fullness) and appetite in order to maintain energy homeostasis.